Identifying Agricultural Frontiers for Modeling Global Cropland Expansion
Abstract
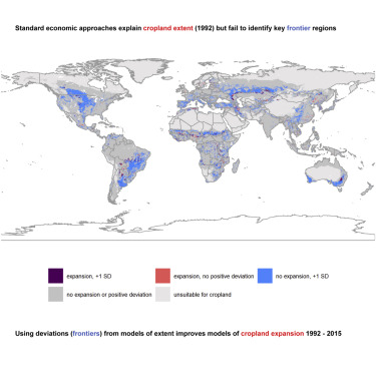
The increasing expansion of cropland is major driver of global carbon emissions and biodiversity loss. However, predicting plausible future global distributions of croplands remains challenging. Here, we show that, in general, existing global data aligned with classical economic theories of expansion explain the current (1992) global extent of cropland reasonably well, but not recent expansion (1992–2015). Deviations from models of cropland extent in 1992 (“frontierness”) can be used to improve global models of recent expansion, most likely as these deviations are a proxy for cropland expansion under frontier conditions where classical economic theories of expansion are less applicable. Frontierness is insensitive to the land cover dataset used and is particularly effective in improving models that include mosaic land cover classes and the largely smallholder-driven frontier expansion occurring in such areas. Our findings have important implications as the frontierness approach offers a straightforward way to improve global land use change models.